Natural Hydrogen Energy
Why Hydrogen?
● Hydrogen is the fuel of the future. It has a high energy conversion efficiency and zero-carbon efficiency. When burned, the only by-product is water.
● Hydrogen is currently used in many industries including the petrochemical industry, manufacture of fertilizer, chemicals, food processing, and transportation.
Additional Uses:
● Decarbonization of the steel and cement manufacturing processes
● Power generation - as backup and in remote locations
● Fuel Cell Systems
● Semiconductor manufacture.
● Hydrogen can be delivered either as a liquid, a gas, or as ammonia by pipeline, tanker, or truck or can be converted at the point of discovery to electricity for transmission by wire.
● Infrastructure required for the transportation of hydrogen includes compression, storage, dispensers, and purification technology.
● There are no hydrocarbons involved in the production of white hydrogen and as such no requirements for carbon capture and sequestration, This makes white hydrogen a very attractive commodity as a transition fuel from both a cost and an environmental viewpoint.
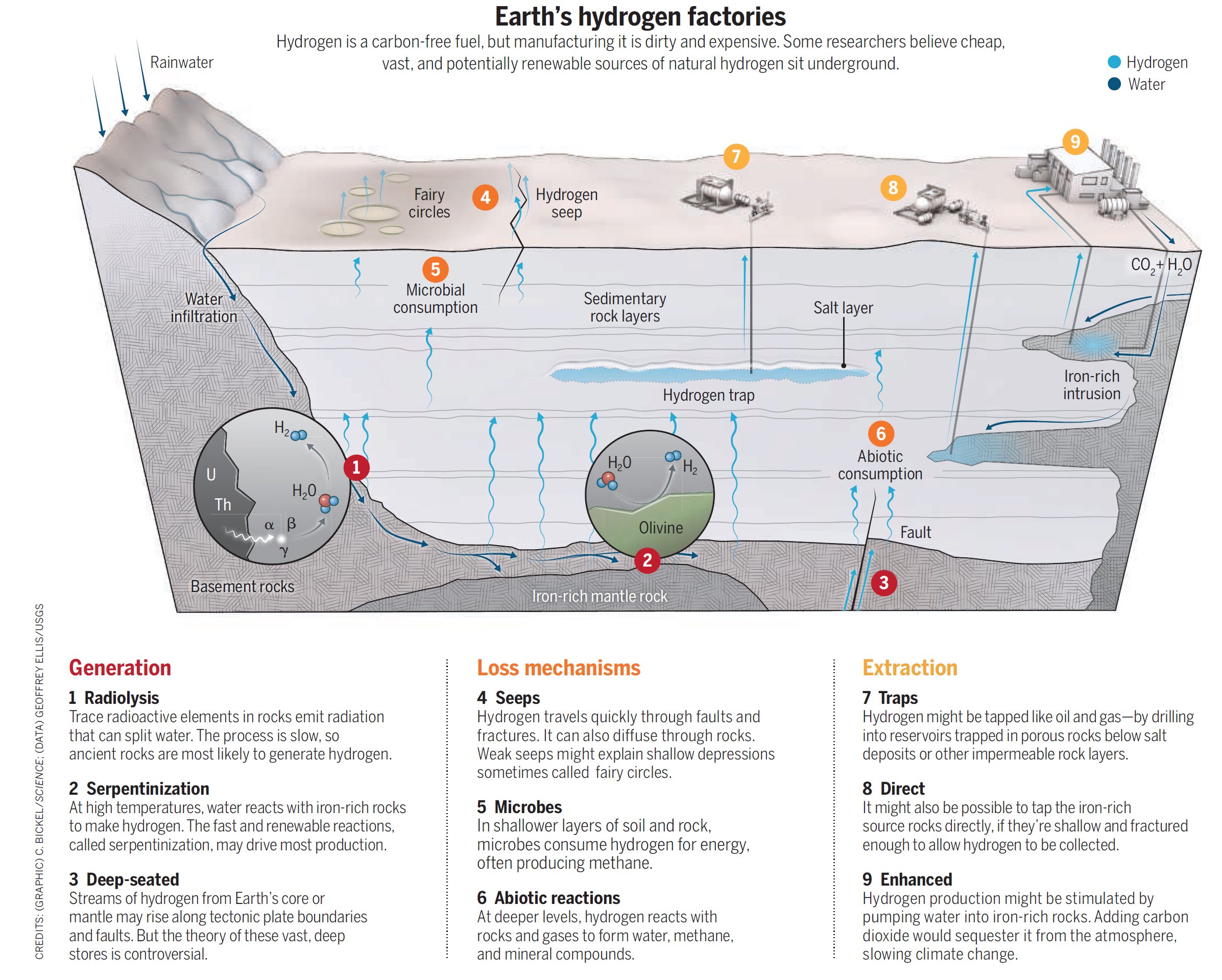
How is Hydrogen Sourced?
● Serpentinization - a process whereby iron-rich rocks (usually olivine and pyroxene) react with water and release hydrogen
● Degassing of deep-sourced hydrogen from the Earth’s Core and Mantle
● Oxidation/reduction processes involving the minerals contained in ancient rocks
● The dissociation of water molecules generates hydrogen due to natural radioactivity.
Natural Hydrogen Exploration Techniques:
● Hydrogen can be explored using similar techniques to those used for natural gas exploration.
● The mechanisms for trapping the gas are similar
● The reservoir rock types are similar
● Migration pathways for the gas from where it is sourced to the trap are similar.
●.The main differences between the natural gas system and the hydrogen system are
● Likely concentration of hydrogen will increase with depth
● The largest accumulations will probably be in Precambrian basement rocks
Successful Exploration Requires:
● Magnetic anomaly
● Gravimetric anomaly
● Location of an aquifer to identify potential areas for the storage of hydrogen

Why Explore the USA?
● Presence of geological formations favorable for hydrogen generation
● Mid-Continent Rift containing iron-rich minerals
● Availability of existing geological and potential field data
● Extensive infrastructure giving ready access to markets.
The most important reason to explore natural and geological hydrogen…
The Environmental Benefits
Regional Abundance
Significant accumulations of natural hydrogen may be found worldwide in a diversified range of geological settings and provide a reliable source of energy.
Extraction
Reduced emission of methane, a potent greenhouse gas, during the drilling process and, depending on gas composition, reduced the use of surface gas processing facilities.
Production Economics
Natural hydrogen is expected to be cheaper to produce than manufactured hydrogen and does not emit CO2. There is also the potential to generate power in a well bore without bringing the hydrogen to the surface.
Hydrogen Delivery
It can be blended with natural gas and transported via existing pipelines.
Energy Storage
Can remain in underground storage until required.
Local Consumption
If discovered remotely, it can be used for power generation thus reducing the requirement for long-distance transportation in addition to enhancing local industry and creating employment.










